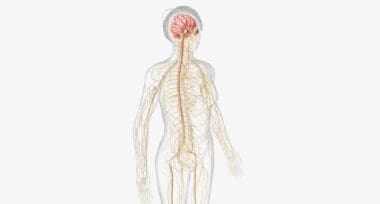
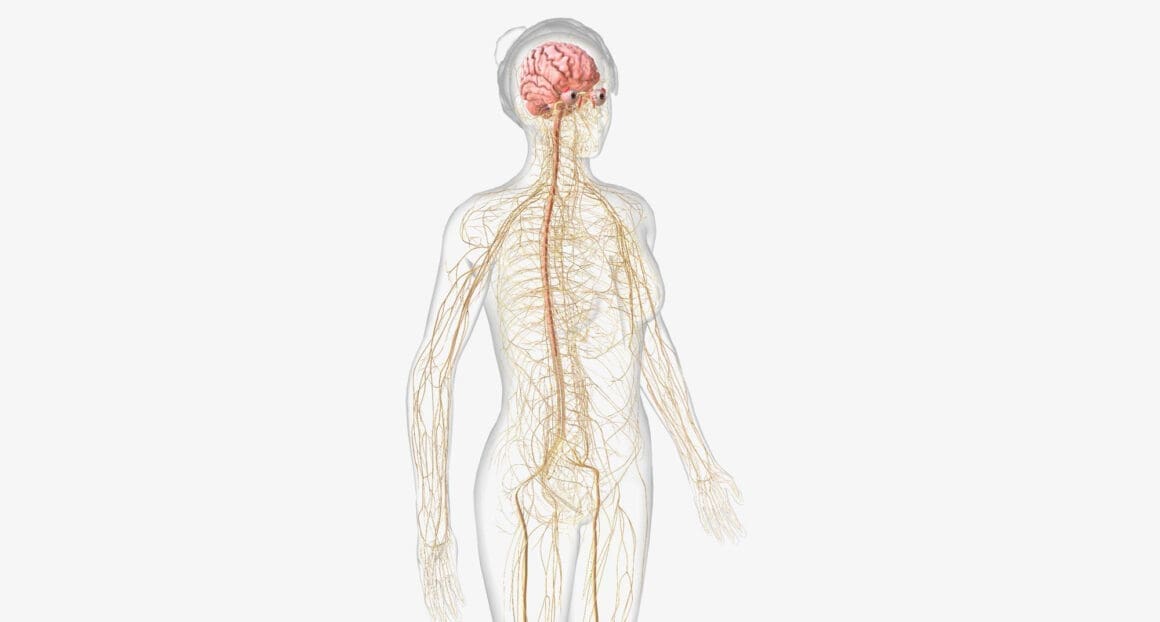
The human nervous system plays a critical role as a communication network within the body, orchestrating a wide range of functions from basic reflexes to complex cognitive processes. At its core, the nervous system is divided into two main components: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, encompassing all neural elements outside the CNS.
The brain, a primary component of the CNS, acts as the command center. Within the brain, the cerebrum is significant as it handles nearly all conscious activities, including decision-making and voluntary movement. Similarly, the cerebellum is pivotal for coordinating physical actions, such as balance and posture. Another vital organ, the hypothalamus, regulates essential bodily processes like temperature and sleep cycles. The hippocampus, meanwhile, is key in forming new memories and learning.
Additionally, the brain’s frontal lobe oversees various functions related to reasoning and emotional regulation, while the temporal lobe is involved in processing auditory information and is vital for language comprehension. The parietal lobe receives and processes sensory input, and the occipital lobe deals with visual data.
On the other hand, the autonomic nervous system, part of the peripheral nervous system, automatically regulates internal organs and glands, influencing heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate without conscious effort. This system functions through a network of neurons, with each playing a distinct role in transmitting information across the body.
Adding to the complexity, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters help relay signals between neurons. These chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine, affect mood, motivation, and mental health. Imbalances in neurotransmitter levels are often linked to mental health disorders, highlighting their crucial role in both physiological and psychological well-being.
The nervous system is also responsible for managing disorders such as Alzheimer’s, characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline, and motor neuron disease, which affects muscular control. Other conditions like multiple sclerosis attack the CNS, disrupting communication between the brain and various bodily systems. Additionally, Parkinson’s disease impairs motor functions, while epilepsy leads to recurrent seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
Understanding these elements offers insight into both the remarkable capabilities and vulnerabilities of the human nervous system. This knowledge underscores the importance of continued research in neurosciences to develop effective treatments and interventions.
Exploring the intricacies of the nervous system reveals the delicate balance it maintains in controlling various body functions. While it masterfully coordinates a multitude of actions and processes, it is also susceptible to a range of disorders that can severely impact quality of life. Continued advancements in understanding neural functions and disorders hold promise for improved therapeutic strategies, highlighting the significance of ongoing research in this vital field.
Source: MedicalNewsToday