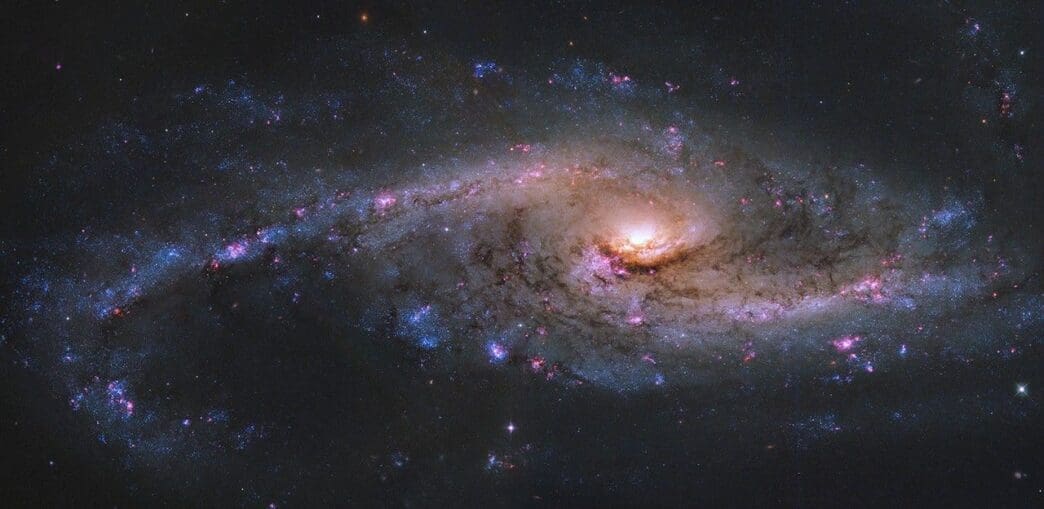
The Hubble Space Telescope recently turned its gaze to a truly mesmerizing object, a starburst galaxy known as NGC 4536. Spiraling gracefully through the vastness of space, this cosmic wonder boasts vibrant blue star clusters and shimmering red patches of ionized hydrogen. It’s an astronomical spectacle that’s as fascinating as it is beautiful.
NGC 4536 resides in the Virgo constellation, about 50 million light-years from Earth. This galaxy is a prime example of a celestial body where star formation is happening at an incredible pace, keeping astronomers intrigued. As Hubble captures its stunning features, the science community eagerly studies the fascinating dance of stars and gas visible in this captivating image.
The Bright Clusters of NGC 4536
NGC 4536’s tantalizing beauty lies in its bright blue star clusters that sprinkle across its spiral arms. These clusters are the birthplaces of hot blue stars that illuminate the surrounding gases with ultraviolet light. The intensity of this light ionizes hydrogen, creating glowing red regions that stand out starkly against the darker lanes of cosmic dust.
It’s not just the colors that are remarkable. The structure of these clusters and their density offer insights into stellar formation. By examining these bright patches, astronomers can learn more about the processes that lead to the creation of stars, making NGC 4536 a stellar laboratory.
An Intermediate Galaxy: Not Quite Barred
NGC 4536 has an intriguing classification as an intermediate galaxy, which means it’s a hybrid between a barred and an unbarred spiral galaxy. This unique structure adds to its charm, making it an interesting subject for astronomical studies.
While many galaxies are classified distinctly as barred or unbarred, intermediate galaxies like NGC 4536 offer a middle ground. Their structure can reveal evolutionary stages and processes not visible in more traditionally categorized galaxies. Their study helps fill gaps in our understanding of galaxy formation.
A Starburst Phenomenon
NGC 4536 is not just any galaxy; it’s a starburst galaxy. This distinct status signifies a rapid pace of star formation that occurs when gas is densely packed into small regions. Such galaxies are laboratories for studying the effects of intense stellar births.
The term “starburst” refers to the galaxy’s exceptional vigor in creating stars. Massive amounts of gases converge to form new stars, using up resources swiftly. These galaxies offer a snapshot of stellar evolution in high gear, providing astronomers a chance to witness dramatic cosmic events.
This type of galaxy fascinates scientists who aim to understand how high rates of star formation contribute to galactic development. These starbursts, often influenced by gravitational interactions or internal gas dynamics, highlight critical stages in galactic lifecycles.
The Nucleus and Its Surrounding Ring
At the heart of NGC 4536 lies its nucleus, surrounded by a ring of vibrant star-forming regions. The bar-like structure pushes gas inward, fueling this celestial furnace.
The dynamics between the nucleus and its surrounding areas are intricate, as the inflow of gas from the galaxy’s spiral arms drives continuous stellar births. Such complex interactions are a focus for researchers exploring the balance of forces that shape galaxies.
Studying this ring and its relationship to the galaxy’s central region provides clues about how galaxies harness and utilize their resources for star formation.
The HII Regions: Red Marvels of Ionized Hydrogen
Within NGC 4536, the bright HII regions, or clouds of ionized hydrogen, glow red against the galaxy’s darker elements. These areas are key indicators of the fierce ultraviolet radiation emitted by newly formed stars, which ionize the surrounding gases.
Understanding these red marvels allows scientists to trace the fierce life cycles of massive stars. Their brilliant red hues mark territories of intense star-making activity, offering windows into the life phases of such stars.
The Historical Discovery of NGC 4536
Discovered in 1784 by William Herschel, NGC 4536’s historical significance is as substantial as its scientific one. Herschel’s discovery added a vital piece to the astronomical catalog of galaxies at a time when the universe was far less understood.
The legacy of this find underscores the importance of early astronomical exploration and its role in shaping today’s advanced studies. This galaxy continues to captivate with its unique structures and dynamic behaviors.
Hubble’s Role in Capturing the Cosmos
The Hubble Space Telescope has once again proven its prowess by capturing NGC 4536 in all its glory. This image is part of a broader project to understand galactic environments, focusing on the relationship between young stars and the cold gas enveloping them.
Hubble’s ability to capture fine details allows astronomers to unravel the complexities of galaxies much more effectively. The data gathered from these images help map out the interaction between various galactic components, shedding light on the cosmic dance of stars and gas.
A Celestial Dance in the Constellation Virgo
Residing in the constellation Virgo, NGC 4536 is 50 million light-years from Earth, nestled in a part of the sky that teems with galaxies. Its position offers astronomers a glimpse into a crowded cosmic neighborhood.
Understanding its place within Virgo provides context for its interactions with nearby galaxies, which could influence its structures and star formation rates. The constellation serves as a backdrop for countless stories written in the stars.
The Virgo constellation itself is an important field of study due to its rich cluster of galaxies, and NGC 4536 adds another layer of intrigue to this celestial expanse.
Galactic Environments and Star Clusters
NGC 4536 offers astronomers a perfect environment to study the interactions between star clusters and molecular clouds within galaxies. These interactions provide clues about star formation processes and the life cycle of stars.
Each cluster within the galaxy tells a different story about the ages and developments of the stars they contain. The coexistence of young and evolved stars within the same region adds a layer of complexity to the galactic tapestry.
A Future of Discovery
As technology advances, the exploration of galaxies like NGC 4536 will deepen our understanding of the universe. New instruments and telescopes will expand our knowledge and possibly illuminate mysteries that still confound us.
The future of astronomy promises to be as thrilling as its past, with the continuation of discovering galaxies that challenge our perceptions and refine our understanding.
The awe-inspiring portrait of NGC 4536 captured by Hubble is more than just a pretty picture. It represents the ongoing exploration of galaxies and the secrets they hold, reminding us of the universe’s endless wonders.