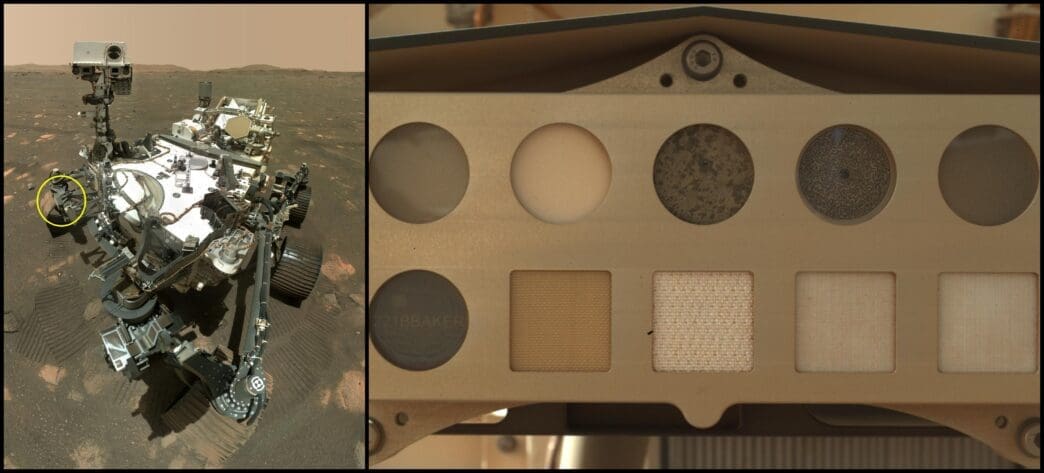
At the forefront of NASA’s cutting-edge exploration is the Perseverance Mars rover, tasked with numerous scientific endeavors on the Red Planet. One intriguing aspect of its mission involves the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals) instrument, which is designed to search for signs of ancient life and study Mars’s geology. Attached to a calibration target on SHERLOC are various spacesuit materials, enabling scientists to assess their durability in the harsh Martian environment.
The calibration target for SHERLOC serves a dual purpose. It not only allows scientists to fine-tune instrument settings using materials with known properties but also provides an opportunity to observe the degradation of spacesuit materials. The materials affixed to the bottom row include a polycarbonate visor piece used in spacesuit helmets, Vectran—a cut-resistant material found in astronaut gloves, the commonly used Ortho-Fabric, and two types of Teflon known for their dust-repelling nonstick properties.
The top row of the calibration target offers a different set of scientific tools: two gallium nitride targets that emit distinct colors under SHERLOC’s laser, a slice of the Martian meteorite Sayh al Uhaymir 008 (SaH 008), a maze for focusing SHERLOC’s camera, and a diffuse transmission target to evaluate how the laser disperses light. This comprehensive setup was captured by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera, a component of SHERLOC mounted on the end of Perseverance’s robotic arm.
Perseverance’s mission on Mars has a key objective of astrobiology, with a focus on searching for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover’s tasks include characterizing the planet’s geology and climate history, laying groundwork for future human exploration, and importantly, collecting and caching samples of Martian rock and regolith. These samples are intended for eventual retrieval by NASA’s Mars Sample Return Program, conducted in partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA). The aim is to bring the samples back to Earth for detailed analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is a significant part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program and its overarching Moon to Mars exploration strategy. This strategy also encompasses the Artemis missions to the Moon, which are crucial in preparing for human expeditions to Mars. The Perseverance rover was constructed and is operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, managed by Caltech in Pasadena, California.
For more information about the Perseverance mission, please visit NASA’s official page on Perseverance.