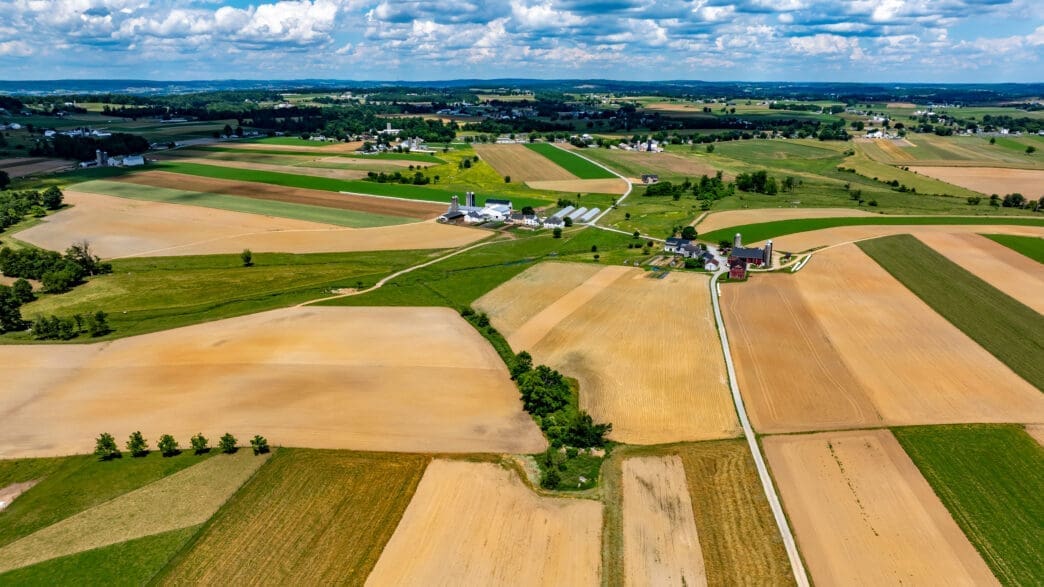
Imagine a world where farmers can get real-time updates on their crops from space. This dream is becoming a reality thanks to a partnership between NASA and ISRO. Their mission? To map farmland from planting to harvest using cutting-edge satellite technology, offering farmers unprecedented insights into crop growth and soil conditions.
The NISAR satellite, a joint project by NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation, is set to launch soon. This groundbreaking mission aims to provide invaluable data on crop health and soil moisture, allowing farmers to optimize their agricultural practices. By harnessing the power of synthetic aperture radar, NISAR will paint a detailed picture of farmland, helping to ensure food security at a global scale.
NASA and ISRO’s upcoming satellite, NISAR, is a game-changer for agriculture. Launching from India’s southeastern coast, it’s designed to deliver around 80 terabytes of data daily. This data is crucial for monitoring large-scale crop growth, even through cloud cover, using advanced radar technology. NISAR’s dual-frequency radar can penetrate crop canopies, giving scientists a clear view of plant health and soil conditions.
Soil moisture is a key factor for healthy crops, and NISAR will provide critical insights into this area. By analyzing radar signals, the satellite can gauge water content in soil and plants, helping farmers manage crops more effectively.
The partnership between NASA and ISRO brings a wealth of expertise, using cutting-edge radar technology to track changes in agricultural lands. This includes monitoring how crops respond to heat waves or droughts, enabling better management strategies during challenging weather conditions.
The collaboration marks a first in flight hardware for NASA and ISRO. It’s a comprehensive effort, with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory leading the U.S. involvement, providing essential components like the radar reflector antenna.
With sensors that can observe small plots of farmland and vast agricultural trends, NISAR aims to offer data that can influence farming policies and practices globally. Its ability to observe Earth’s landmass frequently ensures timely data delivery. The satellite is managed by Caltech, ensuring top-tier engineering and operational excellence.
Farmers worldwide stand to gain significantly from NISAR’s capabilities, as it offers precise data to enhance crop productivity forecasts. By integrating radar measurements with traditional satellite data, agricultural forecasts can become more accurate.
Such detailed information assists governments in estimating crop acreage and yields accurately, paving the way for better resource management. The mission’s high-resolution data ensures farmers have the insights needed to adapt to environmental changes, promoting food security.
NISAR uses advanced radar technologies to provide a deeper understanding of agriculture. With its ability to measure changes in plant structure and soil moisture, it offers a new level of precision in crop monitoring.
This precision extends to helping countries plan planting and irrigation schedules effectively, thus saving on costs and resources. The insights offered by NISAR potentially revolutionize how decision-makers approach agricultural management.
This mission is a prime example of international cooperation in advancing earth sciences. NASA and ISRO have pooled resources and expertise to create a satellite that promises to deliver unprecedented agricultural data.
The integration of NASA’s and ISRO’s technologies showcases the strength of joint ventures in scientific exploration. Both agencies bring unique capabilities that enhance the overall mission’s success. The combined effort ensures the satellite is equipped with the necessary tools to meet its ambitious objectives.
With the integration of science and technology, NISAR will transform agricultural monitoring. Its state-of-the-art radar systems offer insights into soil and crop conditions that were previously unattainable. The mission highlights the potential of scientific collaboration in solving real-world issues.
The satellite’s dual-frequency radar provides versatile data, allowing scientists to distinguish between various crop types and monitor their growth cycles accurately. This integration bridges the gap between scientific inquiry and practical application, offering solutions directly to those who need them the most.
The NISAR satellite ushers in a new chapter for global agriculture. By delivering consistent, actionable insights, it aids in the strategic planning of agricultural activities.
Farmers benefit from real-time data that helps optimize irrigation and planting, ensuring efficient use of resources. This not only boosts productivity but also supports sustainability efforts. The satellite delivers the kind of information that allows for informed decision-making at every level of agriculture.
Looking ahead, NISAR promises to be a vital tool in tackling global challenges related to food security and resource management. As environmental conditions continue to shift, the need for accurate and timely data becomes increasingly critical.
By offering a bird’s-eye view of agricultural landscapes, NISAR empowers decision-makers to plan effectively for the future. Its insights help in anticipating changes and preparing for them in advance, ensuring a resilient food production system.
Innovation is at the heart of the NISAR mission. The satellite represents a leap forward in monitoring technology, offering detailed insights into the earth’s surface that were previously out of reach.
Through high-resolution imagery and comprehensive data collection, NISAR is set to revolutionize how we understand and manage our planet’s resources. It’s a testament to the power of innovation in addressing some of today’s most pressing challenges.
The NASA-ISRO NISAR mission promises to transform our understanding of agriculture. By delivering precise, timely data, it supports smarter farming practices worldwide. This partnership not only represents a scientific achievement but also a significant step towards ensuring global food security in an ever-changing climate.